Advancing Understanding of Neurological Disorders
Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, is one of many public health concerns in Indonesia, as they do in many parts of the world. These complex and debilitating conditions, characterized by the progressive deterioration of the nervous system, present unique challenges in the Indonesian healthcare landscape. Estimates suggest that the prevalence of Alzheimer's disease, the most common form of dementia, is on the rise. However, a total of 86.3% of adults are unaware of characteristics attributed by dementia, rather commonly viewing dementia as a normal part of aging.

Current Incidence of Neurological Disease and Its Predictions
In 2019, there were 26 million newly diagnosed cases of neurological diseases in Indonesia. Among these, stroke accounted for 53.94% of the cases, making it the most prevalent condition. Migraine followed with 17.99%, while idiopathic epilepsy constituted 5.83% of the diagnoses. Alzheimer's disease and other dementias made up 5.46% of the cases, and meningitis accounted for 4.47%. Cases of dementia alone is projected to increase 2.5x from 2016 to 2050. These statistics together highlight the significant burden of neurological diseases and the need for targeted research and interventions.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Neurological Diseases
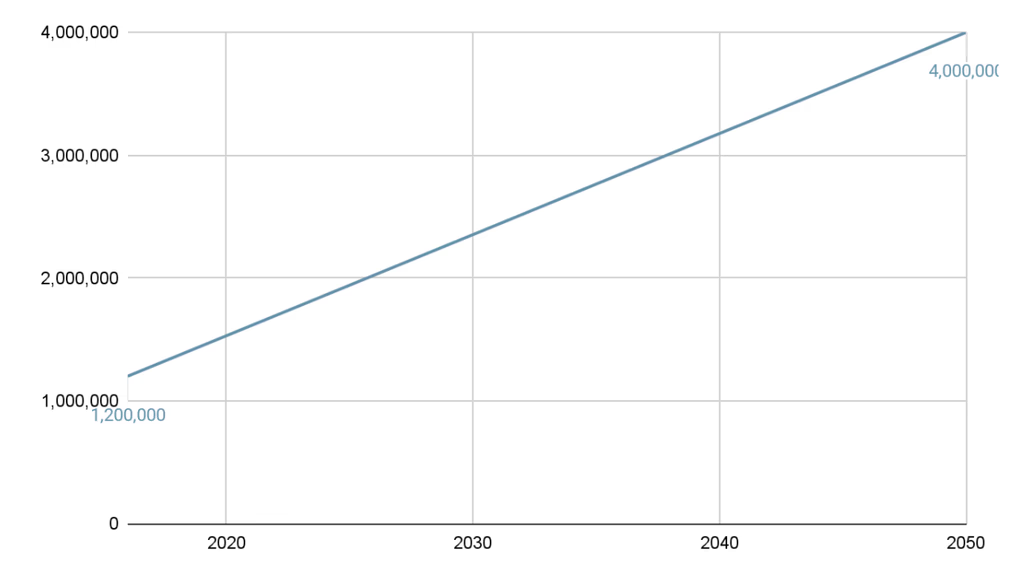
Indonesia was estimated to have 1.2 million people living with dementia in 2016 while it is expected to increase by 2.5 times in 2050.
Current methods for preventing and diagnosing neurodegenerative diseases often prove inadequate due to insufficient resources to identify early and distinguish various forms of neurodegenerative disorders. Additionally, current treatment approaches for neurodegenerative diseases are broad and lack effectiveness. Clinico-genomic research creates opportunities to develop personalized prevention strategies, precise diagnostic tools for early detection, and targeted treatments to manage or slow down cognitive decline by pinpointing genetic and molecular markers.This approach not only tackles the underlying mechanisms of neurodegenerative diseases but also improves predictive models to reduce the overall long-term burden on individuals.












