Building a Brighter Future in Cancer Treatment
Mortality and Burden of Cancer in Indonesia
In Indonesia, as in many other nations, cancer stands as a major public health concern, with the most prevalent types including breast, cervical, lung, colorectal, and liver cancer. The country encounters distinct obstacles in cancer care, such as limited access to programs for early detection, a deficit in healthcare facilities and oncology specialists, and the inaccessible treatment costs for many. Furthermore, a general lack of awareness regarding cancer prevention and the importance of early detection contribute to diagnoses at advanced stages and diminished survival rates. Consequently, the advancement of oncology in Indonesia is geared towards enhancing early detection and screening initiatives, raising public awareness about cancer, and improving the healthcare system along with making treatments more accessible and affordable. Additionally, there is an increasing trend towards combining conventional and novel cancer treatment methods to offer comprehensive care to patients.
The field of clinico-genomic research holds considerable promise for oncology in Indonesia by pinpointing genetic and molecular markers unique to the Indonesian populace that influence cancer susceptibility, progression, and response to treatment. Our studies aim to facilitate personalized treatment approaches, which could significantly enhance treatment efficacy and potentially lower death rates.
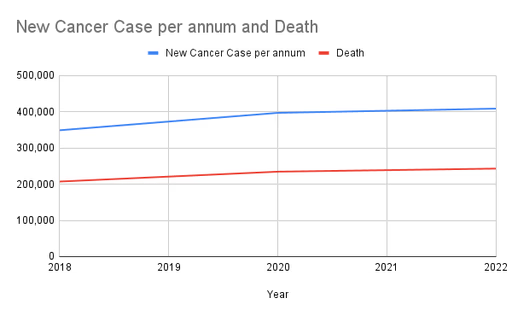
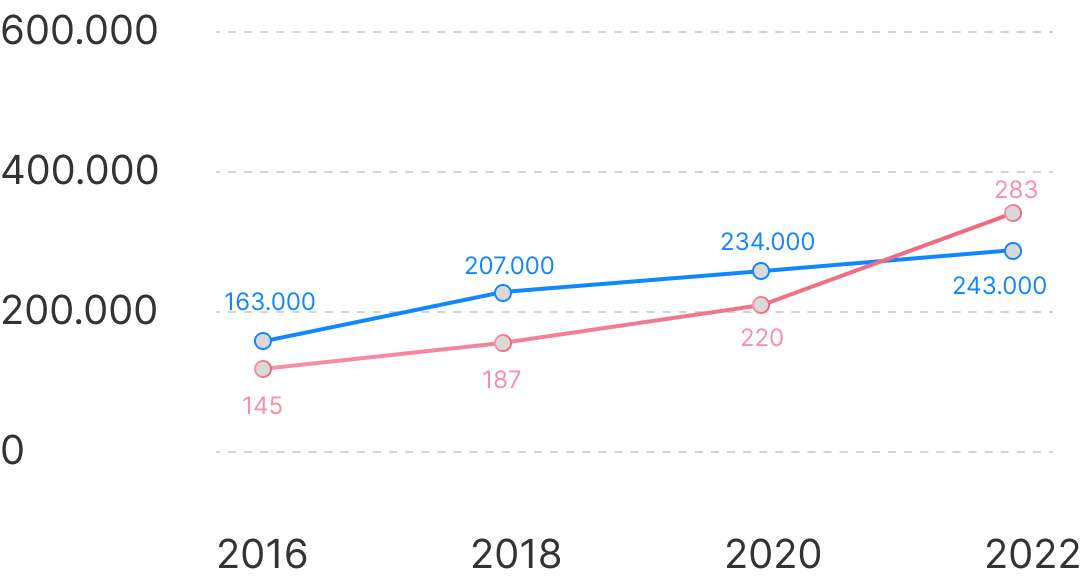
*Globocan data 2018-2022
Globocan Indonesia cancer surveillance
While Indonesia is still lacking in cancer screening and diagnosis practice, cancer cases in Indonesia have been on a constant rise for the past decade.
Precision medicine in oncology
For the patient
- Higher likelihood to demonstrate clinical benefit
- Reduce adverse effects
- Increase survival rate
For hospitals
- More effective use of healthcare resources
- Reduction in hospitalization rates
- Better disease care management
For pharmaceuticals
- Increase success rate of clinical trials
- Improve efficiency in drug development
- Cost reduction
Sources :
- Ajeng Viska Icanervilia, Choridah L, Thea van Asselt, et al. Early Detection of Breast Cancer in Indonesia: Barriers Identified in a Qualitative Study. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention. 2023;24(8):2749-2755. doi:https://doi.org/10.31557/apjcp.2023.24.8.2749
- Suraya A, Nowak D, Sulistomo AW, et al. Excess Risk of Lung Cancer Among Agriculture and Construction Workers in Indonesia. Annals of Global Health. 2021;87(1):8. doi:https://doi.org/10.5334/aogh.3155
- Puspitaningtyas H, Espressivo A, Hutajulu SH, Fuad A, Allsop MJ. Mapping and Visualization of Cancer Research in Indonesia: A Scientometric Analysis. Cancer Control. 2021;28:107327482110534. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/10732748211053464
- Statistics at a Glance, 2022 Top 5 Most Frequent Cancers Number of New Cases 408 661 Number of Deaths 242 988 Number of Prevalent Cases (5-Year). https://gco.iarc.who.int/media/globocan/factsheets/populations/360-indonesia-fact-sheet.pdf
- Prihantono Prihantono, Rusli R, Christeven R, Muhammad Faruk. Cancer Incidence and Mortality in a Tertiary Hospital in Indonesia: An 18-Year Data Review. PubMed. 2023;33(3):515-522. doi:https://doi.org/10.4314/ejhs.v33i3.15
- Worldometer. Indonesia Population. Worldometers.info. Published 2023. https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/indonesia-population/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10416343/#:~:text=According%20to%20the%202020%20Global,(59.08%25)%20(6).












